凌云的博客
行胜于言
LeetCode 算法题 3. 无重复字符的最长子串
分类:algorithm| 发布时间:2016-06-24 12:30:00
题目
给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: "abcabcbb"
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: "bbbbb"
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "b",所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: "pwwkew"
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "wke",所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,"pwke" 是一个子序列,不是子串。
思路
最直观的方法当然就是暴力搜索了,用一个 bool 类型的数组记录某个字符是否出现过, 两层循环搜索给出的字符串,外层循环给出搜索的起点,内层循环检查当前字符是否已经出现过。 这种方法的复杂度为 O(n^2)。
换个思路,将记录字符是否出现过的数组改为 int 类型,-1 表示未出现,否则就是出现过, 其值就是所在的下标。 遍历给出的数组,用当前字符(c)查询 table[c] 的值,若为 -1 则将当前长度增加为 1, 并将当前下标记录到 table[c] 中。 否则将当前长度重置为 i - table[c] (i 为当期下标)并将之前长度到当前长度之间的 table 的值设置为 -1。
for (int j = i - count; j < curIdx; ++j) {
table[s[j]] = -1;
}
count = i - table[c];
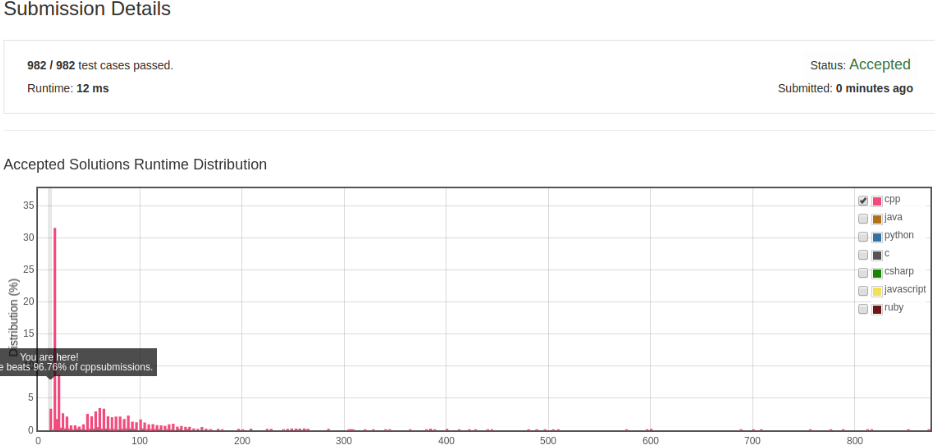
C++ 算法实现
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int table[256];
fill(table, table + 256, -1);
int curIdx = 0;
int count = 0;
int maxCount = 0;
const int size = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i != size; ++i) {
curIdx = table[s[i]];
if (-1 == curIdx) {
++count;
maxCount = max(count, maxCount);
} else {
for (int j = i - count; j < curIdx; ++j) {
table[s[j]] = -1;
}
count = i - curIdx;
}
table[s[i]] = i;
}
return maxCount;
}
};
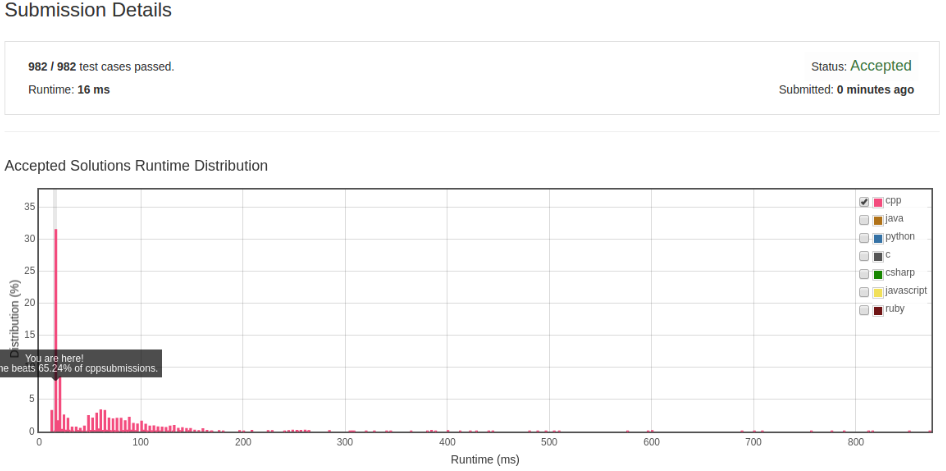
更进一步
在上个算法中当 table[c] 不为 -1 时 执行:
for (int j = i - count; j < curIdx; ++j) {
table[s[j]] = -1;
}
count = i - table[c];
是不必要的,其实只要记录上一个不重复字符的下标,当 curIdx 大于等于不重复下标时, 重新设置不重复的下标。
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int table[256];
fill(table, table + 256, -1);
int maxCount = 0;
int noDupStart = 0;
const int size = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i != size; ++i) {
int current = s[i];
int curIdx = table[current];
if (curIdx >= noDupStart) {
maxCount = max(maxCount, i - noDupStart);
noDupStart = curIdx + 1;
}
table[current] = i;
}
return max(maxCount, int(s.size()) - noDupStart);
}
};